
Clean Agent Systems
CO2 Extinguishing Systems
Fire suppression systems are used to extinguish, control, or in some cases, entirely prevent fires from spreading or occurring. Fire suppression systems have an incredibly large variety of applications, and as such, there are many different types of suppression systems for different applications being used today.


Although they may look similar, fire suppression systems are different from automatic sprinkler systems. Fire sprinklers will typically meet requirements for everyday fire protection in the workplace, but there are instances where suppression systems are the only option.
The main application of suppression systems is to not only extinguish flames but to protect what is important to the organization. Fire suppression systems are utilized when the water from sprinklers can cause irreparable damage to the equipment or area.


Some examples of fire suppression systems and their corresponding NFPA standards include:
Clean Agent: Volatile gaseous fire extinguishant that is electrically nonconducting and that does not leave a residue upon evaporation.
Carbon Dioxide: Does not leave a residue and requires no additional clean-up. Typically used in offices archival rooms, computer rooms, and more. Refer to NDPA 12, Standard on Carbon Dioxide Extinguishing Systems.


Wet Chemical Fire Suppression: When released, forms a type of vapor suppression foam that will prevent re-ignition; mostly used for kitchen applications. Consult NFPA 17A, Standard for Wet Chemical Extinguishing Systems.
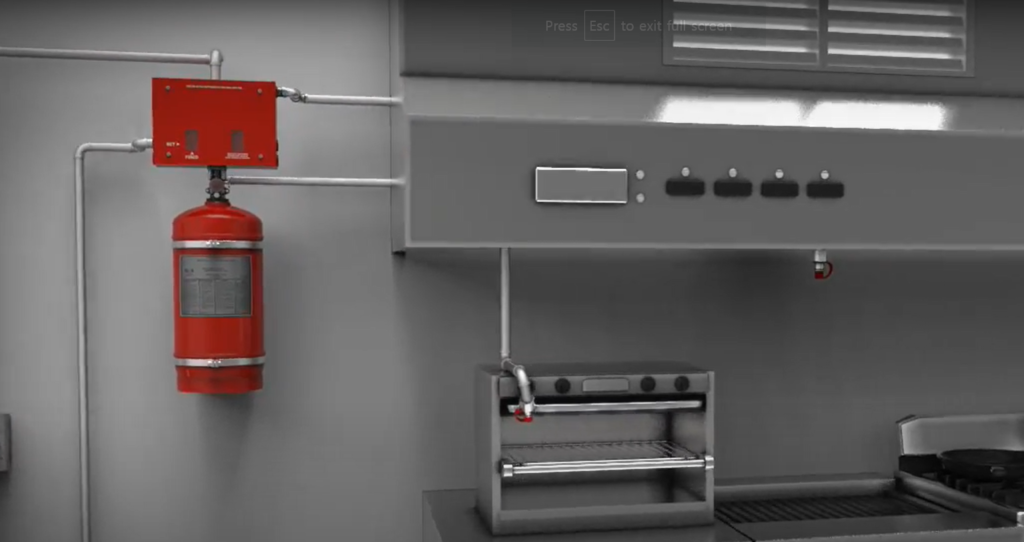

Dry Chemical Suppression: Used in mechanical rooms, furnace rooms, and flammable liquid storage areas, this kind of system works quickly to put out flames caused by combustible or flammable liquids. Additional information can be found in NFPA 17, Standard for Dry Chemical Extinguishing Systems.




Fire extinguishing systems are engineered to detect fires, alert works, and extinguish fires, all in a very short amount of time. Systems can be complicated, but typical elements and components include discharge nozzles, piping, a control panel, warning alarms, hazard signs, detection devices, storage containers, and manual discharge stations.